The Origins
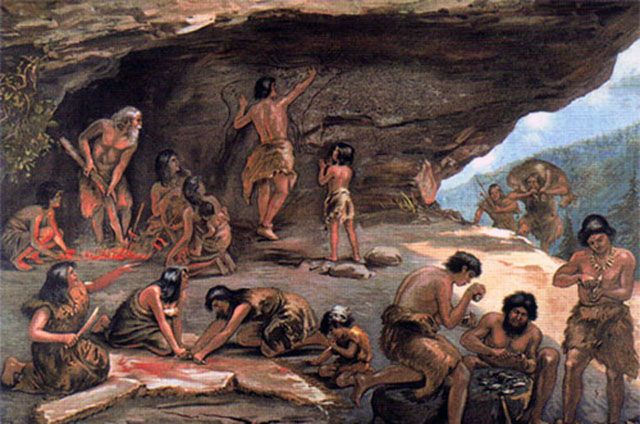
Humans lived in caves as far back as 10,000 B.C. because they needed a place to hide and a place to sleep. In light of the fact that the history of architecture is entwined with the history of humanity as a whole, it is possible to pinpoint the precise beginning of architecture to the Neolithic period, when people ceased living in caves.

Going back to prehistory, we will find that humans made structures that confused people today, where we can find the remains of prehistoric architecture all over the world.
where they were painting on the walls in an artistic way , and they also made shelters from the remaining bones of animales


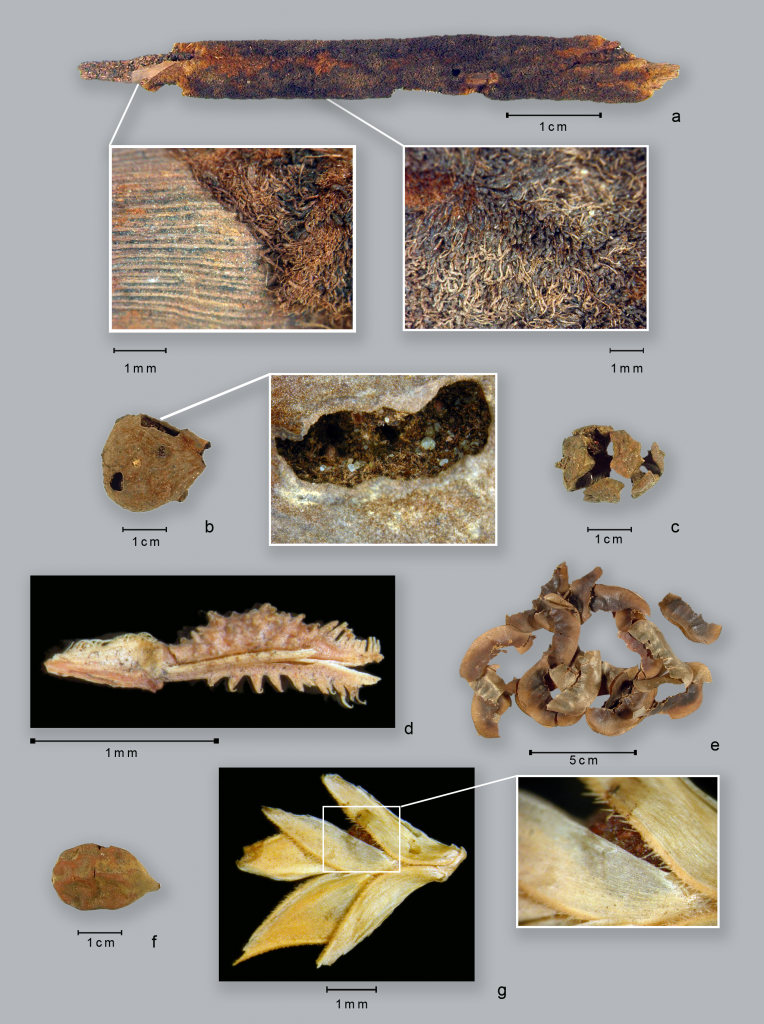
Many individuals believe they are eating large pieces of meat. However, many people actually prefer to consume veggies and grains to meat. Following a thorough chemical examination of 110 pottery fragments unearthed in the Libyan Sahara Desert, which was once a wet savannah with lakes, herds of animals, and lush vegetation, researchers learned this.

The use of defensive walls as protection of the city and building rectangular houses was very common. These houses had a ground floor and a first floor, were built with adobe bricks and the roofs were made by wood and covered by mud.

By 4,000 BC farming had spread across Europe. When people began farming they stopped living in tents made from animal skins and they began to live in huts made from stone or wattle and daub with thatched roofs. Bronze Age people lived in round wooden huts with thatched roofs.
PROTOHISTORY
In, 4.000 – 3.000 B. C. the writing was developed and the societies started to be more affluent . and in this period of time their homes are still made with bricks and adobe

The Egyptians

The earliest artifacts date back to 3.500 B. C. and span a period of over 3.000 years. and they had high-quality homes with lots of rooms where they could live comfortably. Ordinary people lived in simpler buildings made of mud bricks with possibly four rooms; the walls were painted, and the flooring were covered with colored tiles. When it was hot, people may have slept on the flat roof while doing the most of their work outside. The furnishings were quite simple. and along the walls, on brick benches, were the common Egyptians. To store their belongings, they utilized wooden wall pegs or reed boxes.

They believed that the dead had the potential to influence both good and negative events in the lives of the living kin. The deceased relatives were therefore thought of as a living presence. They regularly paid homage to the deceased, offered food and drink to their graves, and made an effort to convey their love and respect for them.

The Greeks

From 1.200 – 146 B. CGreek dwellings during this time period were often straightforward and unadorned. They were constructed with mud bricks and plaster. They believed that achieving excellence in form, detail, and execution would inspire people to work toward reaching their full potential. Ceramic tiles were used to make the roofs. There was no glass in the windows; they were only holes in the wall. One, two, or three rooms were all that the poor could afford. The wealthy Greeks resided in huge homes with numerous rooms. They were typically built around a courtyard and frequently had an additional floor. The dining room and kitchen were located below (called the andron). So was the living room. Upstairs were bedrooms and a room for women called a gynoecium (the women wove cloth there and also ate their meals there away from the men).

The Romans

In Rome, insulae, or apartment buildings, housed the underprivileged. Most had a height of at least five stories. However, they were frequently built improperly, and occasionally their walls cracked and their roofs collapsed. Most people only had one or two rooms to call home. The furnishings were also fairly simple. Always, braziers burning charcoal were used to heat rooms. The locals used restrooms in public places. Most people used water from troughs and fountains in public places. The people of Insulae were forced to purchase hot food from stores because it was too risky for them to cook inside.

And the romans are known for their remarkable engineering feats, be they roads, bridges, tunnels, or their impressive aqueducts.also did a lot of public buildings like the thermal baths, which were used as reunion buildings


Public buildings: circus
The Roman circus was destined for races gladiatorial combats , shows .They also created the basilica as a court of justice for legal proceedings
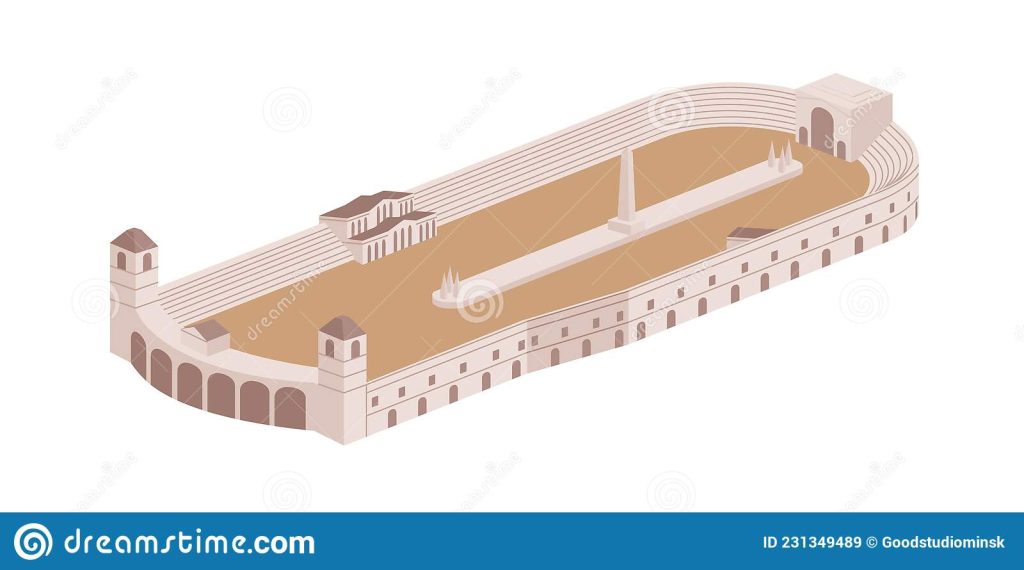
Circus spectacle, its architectural concept and its content, has changed throughout the centuries, following social events and cultural frameworks of time periods.
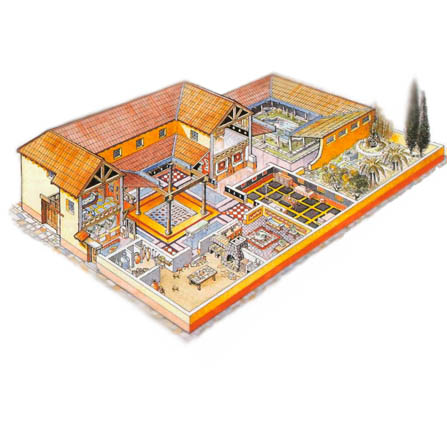
Domus
The domus was the type of house occupied by the upper classes and some wealthy freedmen during the Republican and Imperial eras. They also had gardens and were decorated by mosaics, paintings and sculptures.
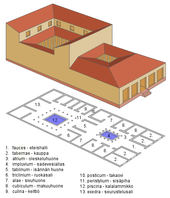
The atrium and the tablinum, which are positioned in the axis of the domus’ entrance, are meant to house clients who come to the boss’s office as part of the morning salutatio. This way, the construction of the domus fits the requirement for social relations created by any family of notables. Therefore, the term «house with atrium and tablinum» is equivalent to «domus.»